COMBINATIONS
=COMBINATIONS(array_1, array_2)
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| array_1 | An array or range or table of numbers or text | {"A";"B";"C"} |
| array_2 | An array or range or table of numbers or text | {1;2;3} |
In the template file, navigate to the Arrays worksheet to see the COMBINATIONS function in action.
✅ Vote to Add Combinatorics Functions to Excel
Description
COMBINATIONS returns an array in which each row of array_1 is paired with each of the rows of array_2 for a total of ROWS(array_1)*ROWS(array_2) combinations. COMBINATIONS works for both text and numeric values (as well as errors and boolean values). Although designed based on the Matlab combinations function, it is also similar to the DAX CROSSJOIN function.
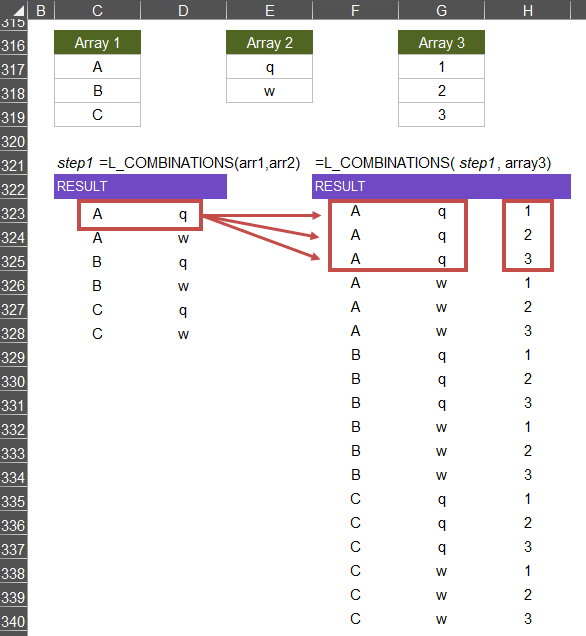
The COMBINATIONS function can be used to form combinations of values between any number of arrays, through nesting the function. For example, to form an array of all combinations of values within 3 different arrays, use:
=COMBINATIONS( COMBINATIONS(array1,array2), array3 )
COMBINATIONS uses two other lambda functions: REPELEM creates the first column (or set of columns) from array_1 by repeating the elements vertically. REPARRAY creates the second column (or set of columns) by repeating the entire array_2 vertically. HSTACK combines the two sets.
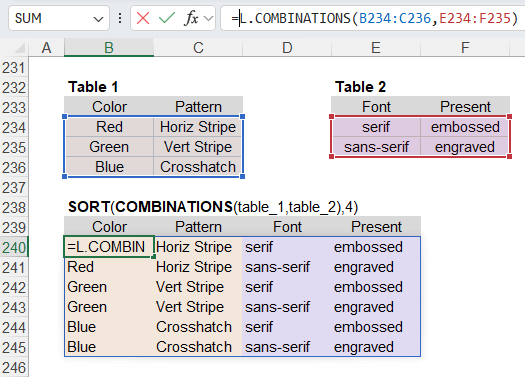
Similar to CROSSJOIN: When the array parameters are multiple columns (we'll call them tables in this case), the behavior of COMBINATIONS(table_1,table_2) is almost exactly the same as the CROSSJOIN(table_1,table_2) function in DAX, except that results may be sorted differently. See the image below.
Finding combinations is useful in many different scenarios. Here are a few example uses:
- Creating a Mesh Grid: In mathematical modeling or 3D plotting, you may have two sets of arrays representing values for X and Y. The combinations of these values creates a grid that you can use for evaluating a Z-value.
- Model Exploration and Optimization: When you have multiple sets of parameters, you may want to try every possible combination of input values to perform a global optimization.
- Experimental Designs: When performing statistical testing with multiple factors, creating an array of all possible combinations of factors allows you to set up a fully crossed design or full factorial design.
- Game Theory and Analysis: You may have a separate set of strategies for two different players and you want to analyze the outcome of all combinations of these strategies.
- Product Mix Decisions: An array may represent different products and a second array various packaging options. Evaluating all combinations may help in decision regarding product mixes.
- Combining Tables: Similar to the CROSSJOIN function in Microsoft DAX (Data Analysis Expressions).
Lambda Formula
This code for using COMBINATIONS in Excel is provided under the License as part of the LAMBDA Library, but to use just this function, you may copy the following code directly into your spreadsheet.
Important: This function also requires REPELEM and REPARRAY
Code for AFE Workbook Module (Excel Labs Add-in)
/** * Return an array of all combinations of rows from two arrays. */ COMBINATIONS =LAMBDA(array_1,array_2, LET(doc,"https://www.vertex42.com/lambda/combinations.html", r_1,ROWS(array_1),r_2,ROWS(array_2), first,REPELEM(array_1,r_2,1), second,REPARRAY(array_2,r_1,1), HSTACK(first,second) ));COMING SOON:
/** * Return an array of all combinations of rows from multiple arrays. */ /* * Inputs: * array_1, array_2: Required. The first two arrays to combine. * [array_3], [array_4], [array_5]: Optional. Additional arrays to include in the combinations. * * Outputs: * Returns an array where each row is a unique combination of rows from the input arrays. * * Requires: REPELEM and REPARRAY */ COMBINATIONS = LAMBDA(array_1, array_2, [array_3], [array_4], [array_5], LET(doc, "https://www.vertex42.com/lambda/combinations.html", version, "1/10/2025 - Multiple optional arrays", // Step 1: Define a helper function to combine two arrays into all possible row combinations. combine_two_arrays, LAMBDA(a, b, LET( r_1, ROWS(a), r_2, ROWS(b), first, REPELEM(a, r_2, 1), second, REPARRAY(b, r_1, 1), HSTACK(first, second) ) ), // Step 2: Initialize with the first two arrays. result, combine_two_arrays(array_1, array_2), // Step 3: Extend the combinations by adding optional arrays if provided. result2, IF(ISOMITTED(array_3), result, combine_two_arrays(result, array_3)), result3, IF(ISOMITTED(array_4), result2, combine_two_arrays(result2, array_4)), result4, IF(ISOMITTED(array_5), result3, combine_two_arrays(result3, array_5)), // Step 4: Return the final combinations. result4 ));
Named Function for Google Sheets
Name: COMBINATIONS Description: Returns an array of all combinations of rows within two arrays Arguments: array_1, array_2 (see above for descriptions and example values) Function: LET(doc,"https://www.vertex42.com/lambda/combinations.html", r_1,ROWS(array_1),r_2,ROWS(array_2), first,REPELEM(array_1,r_2,1), second,REPARRAY(array_2,r_1,1), HSTACK(first,second) )
COMBINATIONS Examples
Test: Copy and Paste this LET function into a cell =LET( vector_1, {1;5;3}, vector_2, {10;50;30}, COMBINATIONS(vector_1,vector_2) ) Result: {1,10;1,50;1,30;5,10;5,50;5,30;3,10;3,50;3,30}
See Also
REPARRAY, REPELEM, COMBINR, PERMUTATIONS
